BANDUNG, itb.ac.id – The Center for Artificial Intelligence at the Bandung Institute of Technology, through the Webinar Series held on Wednesday, May 13, 2020, explained its latest research on “AI for COVID-19 Detection Based on CT-SCAN and X-RAY.” Prof. Dr. Ir. Bambang Riyanto Trilaksono as Professor at the School of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (STEI) ITB as well as Director of the Advanced Robotics Research Laboratory at ITB explained the development of the research.
Personal Documentation
“We also know that there are other test tools, namely the Rapid Test and PCR (for the COVID-19 test) which have been implemented in several countries including Indonesia, but these tests still produce false negatives and false positives in the tests,” explained Prof. Bambang Riyanto regarding the background of this research. He explained that the results of this study would later complement other types of existing tests.
Prof. Bambang, who is the Head of the Informatics and AI Sub-Taskforce for COVID-19 Detection at the Agency for the Assessment and Application of Technology (BPPT), said that this study had already been conducted in China, which stated that CT-SCAN and X-RAY could be used for diagnosing COVID-19. This has the advantage of being relatively high in sensitivity and can then be used to precede virus lab tests.
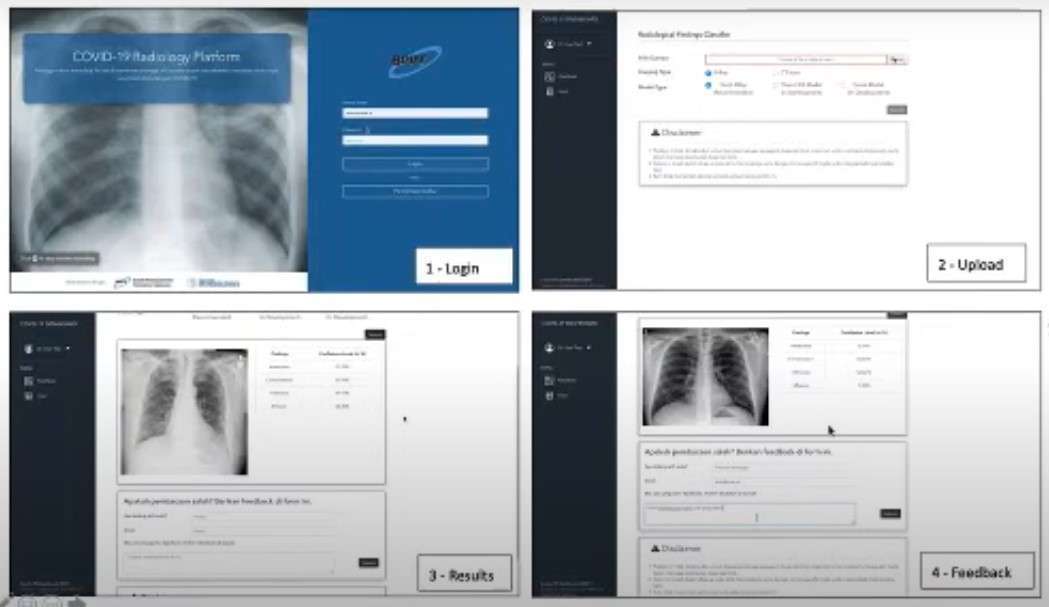
Prof. Bambang also said that we were dealing with a scarcity of medical personnel, including radiologists. So in this case, AI can play a role in the process of identifying patients who are suspected of being exposed to COVID-19 using CT-SCAN and X-RAY results. In general, AI makes improvements to work systems or procedures in the process that must be done by radiologists. According to Prof. Bambang, manually the process of detecting COVID-19 on CT-SCAN and X-RAY can be done for up to 15 minutes by a radiologist. However, with the help of a detection system built with AI, this can be done in 1-2 minutes.
AI in this research is applied through machine learning and deep learning. In simple terms Prof. Bambang explained that it was developed from a simple computation form. This simple computation model is adapted from the work system of neurons in the human brain. Neurons are considered to be the simplest form of computation in humans.
“One of the objects reviewed is the Ground Glass Opacity (GGO), which is a mucous membrane that forms in the lungs of patients affected by COVID-19. This GGO can later be visualized on the processed image to show the location of the affected lung, which then the area can be determined. In addition, the detection of COVID-19 also pays attention to other aspects such as the position and area of consolidation, “said Prof. Bambang.
So far, the AI technology developed in this study already has an interface that makes it easy to use. However, the accuracy in the classification process of CT-Scan and X-Ray images is still in the development stage. The model that has been created has been trained with the data set available online. In the machine learning model, development is being carried out using a data set of COVID-19 patients from Italy, which so far has approximately 160 data. However, to improve accuracy in image processing still requires CT-SCAN and X-RAY results from within the country.
“Currently we are also facing a challenge in order to collect data sets from within the country, from hospitals in Indonesia,” he said. It is mentioned because in the process, several things must be considered, such as the code of ethics and signing of the MoU with the related hospitals. However, Prof. Bambang has targeted that in the next one and a half months this research can be completed.
Reporter: Irfan Ibrahim (Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, 2016). This news has previously been published on the ITB website.