General Description & Curriculum
Master Program in Informatics has some objectives to produce graduates with profiles as Engineers, Managers, Consultants, or Researchers in the field of Informatics who have the following general competences during the early stages of their careers (3-5 years after graduation), namely:
- Our graduates will have critical thinking, innovative, and professional aspects to compete globally in the field of informatics.
- Our graduates will successfully pursue advanced study or engage in professional development.
- Our graduates will have managerial capabilities in research in the field of informatics.
Student outcomes of the Master Program in Informatics are as follows.
- Students will be able to analyze problems in the field of Informatics or other fields of science to identify computing-based solutions.
- Students will be able to design and build computing-based solutions through an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approach
- Students will be able to evaluate computing-based solutions that fulfill the requirements through an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approach.
- Students will be able to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of informatics by engineering and developing specific scientific fields, including:
a. algorithms or computational theory to solve actual and contemporary problems (computer science track), or
b. software engineering, including developing reliable, innovative, and easy-to-maintain large-scale software (software engineering track), or
c. the concept, architecture, and technology of media and mobile devices, including developing the media and mobile device applications using the principles of human and computer interaction as well as good and appropriate software engineering methodologies (media and mobile technology track), or
d. management, processing, and interpretation of large and complex datasets for extraction of critical information and knowledge (data science track), or
e. artificial intelligence concepts, technologies, and applications, including using the suitable tools to deliver an effective and efficient artificial intelligence solution (artificial intelligence track), or
f. the development, operation, and testing of cybersecurity systems (cybersecurity track), or
g. information system governance at the enterprise level to maximize the potential of the system and to minimize its risks using information technology resources efficiently (information systems track), or
h. the analysis, modeling, design, construction, and development of information technology-based systems (information technology track)
i. Development, operation, and security testing of cyber systems (CSec option). - Students will be able to communicate effectively in diverse professional and academic contexts.
- Students will be able to function effectively in team activities by their field of knowledge.
There are 8 (eight) tracks, as follows Computer Science (CS), Software Engineering (SE), Media and Mobile Technology (MMT), Data Science (DS), Cyber Security (CSec), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Information System (IS), and Information Technology (IT).
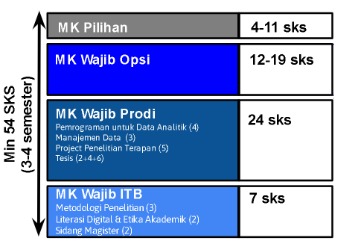
The curriculum of the Master Program in Informatics, comprising a total of 54 credits, is divided into 3 semesters with a maximum load of 18 credits per semester, following the composition below. For the multidisciplinary program scheme and the Double Degree program scheme, the curriculum is structured over 4 semesters.
ITB mandatory : 7 credits
Study Program mandatory : 12 credits of structured courses + 12 credits of Thesis
Track mandatory : 12-19 credits
Elective : 4-11 credits
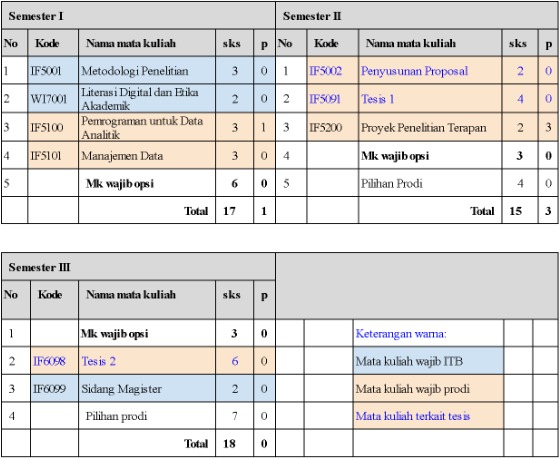
The study period is scheduled within 3 to 4 semesters. The course structure of the Master Program in Informatics for 3 semesters is as follows. Students take 18 credits per semester.
| No | Code | Course | Credits |
| 1 | IF5001 |
Research Methodology
|
3 |
| 2 | WI7001 |
Digital Literacy and Academic Ethics
|
2 |
| 3 | IF5100 |
Programming for Data Analytics
|
3 |
| 4 | IF5101 |
Data Management
|
3 |
| 5 | IF5002 |
Proposal Preparation
|
2 |
| 6 | IF5091 |
Thesis 1
|
4 |
| 7 | IF5200 |
Applied Research Project
|
2 |
| 8 | IF6098 |
Thesis 2
|
6 |
| 9 | IF6099 |
Master's Session
|
2 |
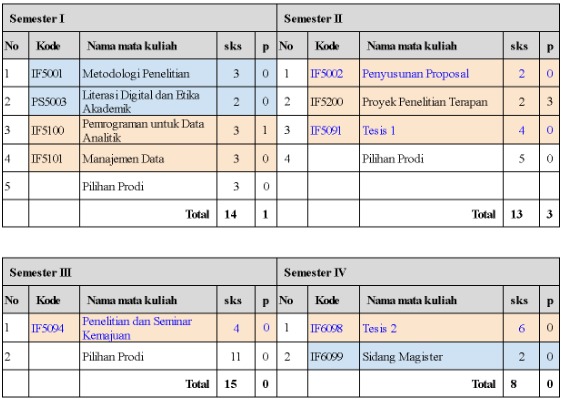
The course structure of the Master Program in Informatics for 4 semesters is as follows. Students take 11–16 credits per semester.
Specifically for the Research-based Master's track, the course composition is arranged according to the following structure, and the curriculum is designed over 4 semesters.
ITB mandatory : 7 credits : 7 sks
Wajib Prodi Study Program mandatory : 12 credits of structured courses + 16 credits of Thesis
Pilihan Electives : 19 credits
The course structure of the Master Program in Informatics for the Research-based Master's track is as follows.
Students in the Computer Science (CS) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing algorithms or computational theories that can address current and real-world problems.
Compulsory courses for the Computer Science (CS) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5110 |
Algorithm Design
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5111 |
Mathematics for Computer Science
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5210 |
Compiler Design
|
3 | 0 |
| 4 | IF5112 |
Advanced Distributed Systems
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Software Engineering (SE) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing large-scale software products that are reliable, innovative, and maintainable.
Compulsory courses for the Software Engineering (SE) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5120 |
Software Requirement Engineering
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5121 |
Software Design
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5220 |
Software Quality
|
3 | 0 |
| 4 | IF5221 |
Software Product Innovation
|
1 | 3 |
| 5 | IF6120 |
Software Evolution
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Media and Mobile Technology (MMT) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing concepts, architectures, and technologies for media and mobile devices, as well as developing applications for media and mobile devices using principles of human-computer interaction and proper software engineering methodologies.
Compulsory courses for the Media and Mobile Technology (MMT) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5130 |
Software Engineering for Game Domain
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5131 |
Multimedia Data Processing and Management
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5230 |
Mobile Technology and Application
|
3 | 0 |
| 4 | IF6130 |
Interactive Media Technology & Application
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Data Science (DS) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing the management, processing, and interpretation of large and complex datasets for the extraction of important information and knowledge.
Compulsory courses for the Data Science (DS) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5140 |
Machine Learning
|
2 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5141 |
Data Mining
|
3 | 1 |
| 3 | IF5240 |
Business Intelligence and Analytics
|
3 | 1 |
| 4 | IF5241 |
Big Data System
|
3 | 0 |
| 5 | IF6097 |
Industrial Internship
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing concepts, technologies, and applications of artificial intelligence, including appropriate tools as effective and efficient AI solutions.
Compulsory courses for the Artificial Intelligence (AI) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5150 |
Advanced Artificial Intelligence
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5151 |
Mathematics for Artificial Intelligence
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5250 |
Deep Learning
|
3 | 1 |
| 4 | IF5251 |
Artificial Intelligence in Production
|
3 | 0 |
| 5 | IIF6150 |
Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence
|
3 | 0 |
| 6 | IF6151 |
Artificial Intelligence Individual Project
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Cybersecurity (CSec) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics, particularly in the development, operation, and testing of cybersecurity systems.
Compulsory courses for the Cybersecurity (CSec) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5161 |
Data and Software Security
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF6160 |
System Security & Privacy
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5260 |
Digital Forensics
|
3 | 0 |
| 4 | IF5160 |
Cybersecurity Operations
|
3 | 0 |
| 5 | IF6161 |
Cybersecurity Individual Project
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Information Systems (IS) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing Information Systems governance at the enterprise level to maximize system potential and minimize risks through the efficient use of Information Technology resources.
Compulsory courses for the Information Systems (IS) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5170 |
Digital Strategy
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5171 |
System Thinking
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5270 |
Applied Artificial Intelligence for Enterprise
|
3 | 1 |
| 4 | IF5271 |
Information System Sustainability
|
3 | 0 |
| 5 | IF6170 |
Data Governance
|
3 | 0 |
Students in the Information Technology (IT) track are expected to develop research-based knowledge and technology in the field of Informatics by designing and developing the analysis, modeling, design, construction, and advancement of information technology-based systems.
Compulsory courses for the Information Technology (IT) track:
| No | Code | Matakuliah | Credits | P |
| 1 | IF5180 |
Digital Twin Technology
|
3 | 0 |
| 2 | IF5181 |
Information Technology Platform
|
3 | 0 |
| 3 | IF5280 |
Digital Security, Privacy, and Forensics
|
3 | 0 |
| 4 | IF6180 |
Digital Transformation and Enterprise Architecture
|
3 | 0 |
Informasi Umum
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, Oktober 2023
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, Juli 2023
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, April 2023
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, Oktober 2022
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, Juli 2022
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, April 2022
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, Oktober 2021
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, Juli 2021
Wisudawan Program Magister Informatika, April 2021
Program Penyatuan Sarjana Magister (PPSM) memiliki sasaran meningkatkan jumlah mahasiswa Program Sarjana ITB yang melanjutkan studi di Program Magister dengan masa studi sesuai target program integrasi. Hal ini dilakukan untuk mencapai salah satu target indikator Renstra ITB 2021-2025 yang ingin dicapai pada tahun 2025 yaitu persentase jumlah mahasiswa Pascasarjana sebesar 40%. Berdasarkan pemenuhan kompetensi dasar computing, terdapat skema umum atau penyatuan Sarjana-Magister serumpun dan tidak serumpun dengan Program Studi Magister Informatika, yang dibagi dalam tiga kategori sebagai berikut:
- Linier, untuk mahasiswa Prodi S1 yang sudah memenuhi semua kompetensi dasar. Berdasarkan kurikulum, prodi S1 yang memenuhi adalah prodi S1 dari STEI-K (Teknik Informatika dan Sistem & Teknologi Informasi).
- Semi-linier, untuk mahasiswa Prodi S1 yang sudah memenuhi sebagian kompetensi dasar. Berdasarkan kurikulum, prodi S1 yang memenuhi adalah prodi S1 dari STEI-R (Teknik Elektro, Teknik Telekomunikasi, Teknik Biomedis, Teknik Tenaga Listrik).
- Tidak linier, untuk mahasiswa Prodi S1 yang belum memiliki kompetensi dasar. Prodi lain di luar STEI pada umumnya dapat dikategorikan ke dalam kategori tidak linier, kecuali prodi-prodi yang memiliki kompetensi dasar computing. Evaluasi terhadap prodi di luar lingkungan STEI apakah termasuk dalam kategori semi linier atau tidak linier akan dilakukan per kasus pada saat mahasiswa prodi S1 yang terkait mendaftar pada program ini.
Tabel Kompetensi dasar Computing
| Kompetensi dasar | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| Pemrograman |
|
| Basis Data |
|
| Matematika Diskrit |
|
| Sistem Komputer |
|
Struktur Mata kuliah Prodi Magister Informatika PPSM sebagai berikut.
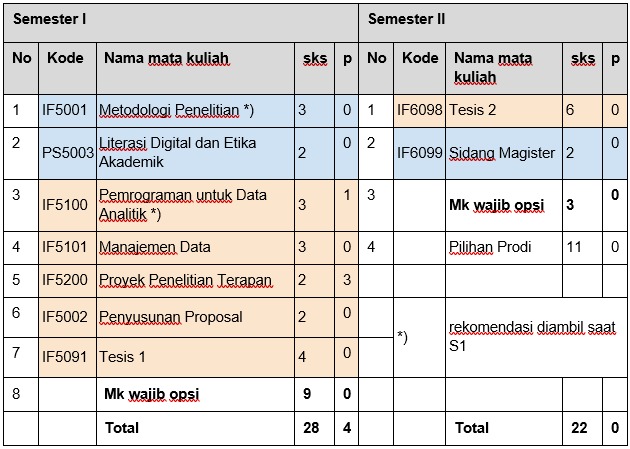 Mahasiswa PPSM wajib melaksanakan TA Tesis berkelanjutan, yaitu pelaksanaan TA di program sarjana dan Tesis di program magister dengan topik yang berkelanjutan sehingga merupakan bagian dari pekerjaan/penelitian di area yang sama. Berkaitan dengan kategori peserta program PPSM, aturan untuk melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan didefinisikan sebagai berikut.
Mahasiswa PPSM wajib melaksanakan TA Tesis berkelanjutan, yaitu pelaksanaan TA di program sarjana dan Tesis di program magister dengan topik yang berkelanjutan sehingga merupakan bagian dari pekerjaan/penelitian di area yang sama. Berkaitan dengan kategori peserta program PPSM, aturan untuk melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan didefinisikan sebagai berikut.
- Linier: mahasiswa wajib melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan dengan topik dan pembimbing yang sama.
- Semi-linier: mahasiswa disarankan melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan dengan topik yang dimungkinkan bersifat multidisiplin dengan bidang program sarjana mahasiswa yang bersangkutan dan dengan tim pembimbing yang dapat berasal dari prodi sarjana mahasiswa ybs. dan dari prodi Magister Informatika. Namun jika tidak, maka mahasiswa wajib melaksanakan TA dengan topik di bidang komputasi, walaupun tidak berkelanjutan dengan topik tesis di Prodi Magister Informatika dan dapat dilaksanakan dengan pembimbing yang berbeda.
- Tidak linier: mahasiswa disarankan melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan dengan topik yang dimungkinkan bersifat multidisiplin dengan bidang program sarjana mahasiswa yang bersangkutan dan dengan tim pembimbing yang dapat berasal dari prodi sarjana mahasiswa ybs. dan dari Prodi Magister Informatika. Namun jika tidak, maka mahasiswa disarankan mengambil topik TA di bidang komputasi, walaupun masih dimungkinkan untuk mengambil topik lain di luar bidang komputasi sesuai dengan bidang prodinya, sehingga dapat dilaksanakan dengan pembimbing yang berbeda dengan tesis.
Rancangan pengelolaan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan secara umum adalah sebagai berikut.
- Persyaratan pembimbing:
TA Tesis Berkelanjutan dilaksanakan dengan pembimbing yang sama baik untuk TA maupun Tesis. Jumlah maksimum pembimbing adalah 2 orang, baik untuk TA maupun Tesis. Jika pembimbing hanya 1 orang, maka pembimbing tersebut harus eligible sebagai pembimbing utama di prodi sarjana dan Prodi Magister Informatika. Jika pembimbing 2 orang, maka salah satu pembimbing harus eligible sebagai pembimbing utama di Prodi Magister Informatika dan aturan urutan pembimbing utama dan pendamping mengikuti aturan di prodi sarjana dan Prodi Magister Informatika. Daftar dosen pembimbing untuk Prodi Magister Informatika dapat diakses pada Dosen Pembimbing Tesis Magister Informatika ITB. - Persyaratan topik:
- Topik TA Tesis Berkelanjutan harus berada dalam cakupan bidang komputasi.
- Topik TA Tesis Berkelanjutan harus mempertimbangkan tingkat keilmuan dan kedalaman yang sesuai dan harus dapat dibagi dengan jelas target untuk proses TA di program sarjana dan target proses tesis di program magister.
- Topik TA Tesis Berkelanjutan harus sesuai dengan jalur pilihan mahasiswa di Prodi Magister Informatika.
- Topik TA Tesis Berkelanjutan dapat berasal dari para calon dosen pembimbing atau dapat berasal dari usulan mahasiswa. Jika usulan berasal dari mahasiswa, maka harus dikonsultasikan dan disetujui oleh pembimbing.
- Pendataan mahasiswa:
Sebelum semester 7 pada program sarjana mahasiswa dimulai, tim implementasi PPSM mengadakan pertemuan dan sosialisasi dengan seluruh mahasiswa peserta program PPSM yang sudah waktunya mengambil TA pada semester 7. Mahasiswa diminta untuk menyerahkan perencanaan pengambilan TA Tesis untuk mendapatkan informasi tentang peserta-peserta yang akan mengambil TA Tesis Berkelanjutan, terutama untuk mahasiswa dari kategori semi-linier dan non-linier. - Prosedur alokasi topik dan pembimbing:
- Untuk semua mahasiswa yang akan melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan, tim implementasi PPSM berkoordinasi dengan semua tim pelaksana TA di semua prodi mahasiswa terkait dan tim pelaksana tesis Prodi Magister Informatika untuk mengkoordinasikan pengalokasian topik TA Tesis dan pembimbing untuk mahasiswa ybs.
- Proses alokasi topik dan pembimbing TA Tesis dapat menjadi kasus khusus pada pengalokasian topik dan pembimbing TA di prodi sarjana mahasiswa dan prosedurnya dapat disesuaikan dengan prosedur di prodi sarjana masing-masing dengan syarat memastikan bahwa syarat topik (lihat butir 2) dan pembimbing (lihat butir 1) terpenuhi.
- Setelah mahasiswa dialokasikan topik dan pembimbing, mahasiswa melaporkan proposal perencanaan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan yang telah ditandatangani oleh mahasiswa dan pembimbing ke tim implementasi PPSM.
- Proses alokasi topik dan pembimbing dapat dimulai sebelum semester 7 dimulai dan sudah harus selesai selambat-lambatnya minggu ke-7 semester 7 program sarjana mahasiswa.
- Pengambilan mata kuliah terkait:
a. Pengambilan mata kuliah TA di prodi sarjana- Asumsi: Terdapat mata kuliah TA-I di semester 7 dan TA-II di semester 8 di setiap prodi sarjana.
- Mahasiswa melaksanakan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan porsi untuk program sarjana dengan mengikuti prosedur pelaksanaan TA di prodi masing-masing dengan catatan: dalam penyampaian proposal TA, harus dicakup juga topik dan perencanaan untuk sampai pelaksanaan Tesis.
- Mahasiswa melakukan pengambilan mata kuliah TA-I pada semester 7. Seluruh atau sebagian proses alokasi topik dan pembimbing dapat dilakukan pada semester ini (lihat butir 4.d.)
- Pengambilan mata kuliah TA-II dilakukan pada semester 8.
- Pengambilan mata kuliah Metodologi Penelitian dan Tesis dilaksanakan setelah mahasiswa berubah status menjadi mahasiswa Prodi Magister Informatika. Pengambilan mata kuliah Metodologi Penelitian dilakukan pada semester 1 dan mata kuliah Tesis diambil pada semester 2 dan dilaksanakan sesuai prosedur dan aturan yang berlaku di Prodi Magister Informatika.
Catatan: Dalam penyampaian proposal Tesis, harus disampaikan hasil-hasil dari TA yang akan dilanjutkan dalam Tesis.
- Selama pelaksanaan TA Tesis Berkelanjutan, mahasiswa tidak diperkenankan berganti topik dan pembimbing, khususnya dari TA ke Tesis. Penggantian topik atau pembimbing dapat dilaksanakan dengan alasan kedaruratan tertentu dan mengikuti prosedur yang ditetapkan oleh Prodi Magister Informatika dan diketahui oleh tim implementasi PPSM.
Program studi Magister Informatika Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB melaksanakan Double Degree Program (DDP), bekerja sama dengan beberapa perguruan tinggi mitra di luar negeri. Mahasiswa peserta DDP dapat memperoleh gelar dari dua perguruan tinggi sekaligus yaitu gelar ITB dan gelar dari perguruan tinggi mitra ITB di Luar Negeri.
Mahasiswa dapat memulai dari program studi Magister Informatika ITB dan mengikuti perkuliahan di ITB pada tahun pertama sesuai kurikulum Magister Informatika ITB, lalu mahasiswa akan melanjutkan perkuliahan di perguruan tinggi mitra di luar negeri pada tahun kedua. Hal ini berlaku sebaliknya untuk mahasiswa dari perguruan tinggi mitra, yaitu tahun pertama mengikuti perkuliahan sesuai kurikulum di program studi universitas awal, lalu mahasiswa akan melanjutkan kuliah di ITB pada tahun kedua.
Pada saat ini, program studi Magister Informatika ITB menawarkan DDP dengan 4 perguruan tinggi mitra sebagai berikut:
1. Toyohashi University of Technology – Computer Science & Engineering (Japan)
DDP TUT-ITB telah dimulai secara formal dengan Agreement for Double Master’s Degrees between Toyohashi University of Technology (TUT) and Institut Teknologi Bandung (ITB) tanggal 18 Agustus 2023, dan Addendum Agreement for Double Master’s Degrees between Computer Science and Engineering TUT and Informatics ITB tanggal 22 Agustus 2023.
Link web: https://www.tut.ac.jp/english/introduction/publications.html
2. Singapore Management University – Master of IT in Business (Singapore)
Program ini sudah terdaftar pada beasiswa LDPD Program Double Degree.
https://lpdp.kemenkeu.go.id/storage/beasiswa/kebijakan-umum/file/public_policy_file_1737168598.pdf
Beasiswa lainnya: Soegiarto Adikosoemo Postgraduate Scholarship
3. Grand Valley State University – College of Computing
Link web: https://www.gvsu.edu/computing/itb-international-agreements-191.htm
4. La Trobe University –
Administrative Form
- Formulir Pembimbing dari Luar ITB
- Formulir Penggantian Topik/Pembimbing/Tambah Pembimbing
- Formulir Usulan Seminar Tesis S2 Informatika (offline)
- Formulir Usulan Seminar Tesis S2 Informatika (online)
- Form Persyaratan Sidang Tesis
- Formulir Usulan Sidang Tesis S2 Informatika (offline)
- Formulir Usulan Sidang Tesis S2 Informatika (online)
- Link formulir upload cek plagiasi paper mahasiswa Magister Informatika
Panduan dan Aturan
- Panduan Seminar Tesis Secara Daring
- Panduan Sidang Tesis Secara Daring
- Panduan Pelaksanaan Sidang/Seminar Pascasarjana
- Template Proposal Tesis S2 IF
- Sistematika Laporan Kemajuan IF5091/IF5092 Pelaksanaan Penelitian 1/ 2
- Template Proposal Riset MBR
- Panduan Wawancara MBR
- Panduan Pelaksanaan Tesis S2 IF (2022)
- Pedoman KP Industri S2 IF & Administrasi